11 - 14 February 2025. Ibadan, Nigeria. The Global Forum for Agricultural Research and Innovation (GFAiR) organised a second proposal write shop to target funding opportunities on Forgotten Foods. This follows a first proposal write shop in Winneba (Ghana) in January.
The main aim of this meeting was to apply for
- The INCiTiS-FOOD Open Call for Local Innovation Hubs Deadline: March 20th, 2025 The INCiTiS-FOOD Open Call aims to attract Local Innovation Hubs (LIHs), small consortia that must comprise a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 3 legal entities, such as NGOs, cooperatives, and educational institutions. These consortia will co-create and implement innovative solutions tailored to sustainable and circular food systems, fostering collaboration and addressing local food system challenges. A webinar for Q&A will be held on 5th March
- The One planet call for proposals: Sustainable Food systems Project proposals should drive meaningful change and support the achievement of the following impacts: - Knowledge and Advocacy: (1) Promote the uptake of SFS Programme Knowledge Hub resources and tools among global and national stakeholders. (2) Represent the Youth Voice in the shaping of the emerging OPN flagship initiative on leveraging sustainable public procurement to advance sustainable food systems, with a current focus on school meals. (3) Act as a multiplier by supporting the SFS Programme through communication activities (social media). Deadline: March 3rd, 2025
- Third UK Research Grant Competition: Global Centre on Biodiversity for Climate (GCBC) - Theme 1: Using biodiversity to improve the climate resilience of agricultural, food and bioeconomy value chains. The Concept Note application window will close on March 16th.

Extract of the program:
10/02 Concept note of the proposal
K-TOMFonio-Project. Ponic Technologies for Developing Human and Poultry Diets from Fonio Seeds and King Tuber Oyster Mushroom
The project shall demonstrate innovative ponic technologies for producing human and poultry diets from forgotten crops such as fonio and KOM at urban and peri-urban environments in Nigeria. The technologies are cost-effective and shall utilize minimal space and time to produce highly nutritious diets in the study environments. The project shall create potential income channels for urban and peri-urban farmers, new research skills for the participating researchers and introduce highly nutritious human and poultry diets to end users.
11/02 Panel discussion: Forgotten foods and the research - private sector nexus

Objective:
- Share examples on how the private sector can take up research outcomes related to Forgotten Foods
- Research priorities
- How to link up with the private finance sector
- Public funding opportunities
Online Speakers: (International Nutrition and Food experts)
- Dr. Habiba Wassef (MD), ANS (African Nutrition Society) Living Legend of the International Union of Nutrition Sciences ; Health and Nutrition Policy in Sustainable Development ; Chair, National Nutrition Sciences Committee Egypt
- Robert Fungo, President, The Federation of African Nutrition Societies (FANUS), School of Food Technology, Nutrition & Bio-Engineering, Makerere University Kampala, Uganda
- Dr. Stella Iwuagwu: Executive Director at Centre for the Right to Health
- Owole Fatunbi - Forum for Agricultural Research in Africa: FARA Forgotten Foods Dgroups / Community of Practice
- Babafemi Oyewole - CEO Pan African Farmers Organization (PAFO) Kigali, Rwanda
The GFAiR-Ibadan Hybrid Meeting on "Forgotten Foods and the Research-Private Sector Nexus" brought together experts to discuss the role of forgotten foods in food security, nutrition, and commercialization. Dr. Habiba Hassan-Wassef emphasized the importance of tailoring approaches to different ecological zones and integrating forgotten foods into modern food systems, while Robert Fungo highlighted the private sector's role in adding value through research, market assessment, and processing innovations. Dr. Stella Iwuagwu discussed the "food as medicine" concept, urban farming challenges, and the need for local food production. The meeting addressed marketing, innovation, policy advocacy, and private sector engagement to increase the visibility, production, and commercial viability of forgotten foods. Action points included social media awareness campaigns, farmer-led enterprises, policy engagement, and financial initiatives to promote forgotten foods across Africa sustainably.
Download the summary (7 pp.)
12/02 I-Youth agribusiness
- Presentation (on site) by Noel Mulinganya, IITA Program Manager - Youth Program/Technologies for African Agricultural Transformation (TAAT).
The IITA Youth Agripreneurs (IYA) presentation highlights initiatives aimed at engaging African youth in modern, sustainable, and profitable agribusiness to address unemployment, improve livelihoods, and enhance food security. The IYA model provides institutional support, technical assistance, and access to economic opportunities within agricultural value chains. Key projects include Innovative Youth in Agriculture (I-Youth), ENABLE-TAAT, and the Start Them Early Program (STEP), which focuses on training young people in agribusiness and technological advancements. The Agribusiness Park initiative fosters startup growth by creating supportive ecosystems for agripreneurs, with established ventures in aquaculture, horticulture, and livestock production. Over the past decade, IYA has trained 44,872 direct participants, created 85,616 jobs, and supported 12,410 youth-led agribusiness startups. The STEP program integrates agricultural education into schools, ensuring sustainability through teacher training and community engagement. The presentation underscores the need for innovative financing, institutional mindset shifts, and multi-dimensional job creation to sustain youth involvement in agribusiness.
12/02 Urban agriculture: business for young entrepreneurs?

- Presentation (on site) by Angel Adelaja, CEO, Fresh Direct, Nigeria
The FreshDirect Urban Agriculture presentation introduces an innovative approach to urban farming through container farms, utilizing hydroponics and vertical farming to grow fresh, organic produce closer to urban markets. By integrating technology, sustainability, and efficiency, the model reduces land and water use while addressing food security challenges, post-harvest losses, and food import dependency. The initiative promotes synergy between urban, peri-urban, and rural agriculture, emphasizing productivity, sustainability, and economic impact. FreshDirect aims to empower youth, particularly women, through hands-on training and job creation, making agribusiness more accessible. Their growth strategy includes expanding container farms, establishing a retail and training hub, and integrating digital solutions like an interactive farm management app for growers and investors. To scale, they propose policy advocacy, incentives, coordination, and aggregation centers, ensuring long-term urban farming sustainability.
(below: 10 April 2018. CTA Brussels Development Briefing no. 50 on “Growing food in the cities: Successes and new opportunities”. This Briefing was organised by the ACP-EU Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation (CTA), in collaboration with the European Commission / DEVCO, the ACP Secretariat, and CONCORD.)
13/02 The new Odisha Government scheme on neglected crops and forgotten foods.
- By Dinesh Balam, Program Officer - Policy Advocacy and Coordination - Revitalizing Rainfed Agriculture Network. WASSAN (Watershed Support Services and Activities Network) is the anchoring secretariat of CoFTI (the Coalition of food systems transformation in India initiative).
The WASSAN (Watershed Support Services and Activities Network) presentation outlines its initiatives in natural farming, millet promotion, seed systems, and rural development to support sustainable agriculture in Odisha, India. The Odisha Millets Mission focuses on conserving and promoting millet landraces, increasing millet consumption, and integrating them into public food programs like the PDS and mid-day meals. WASSAN has conducted large-scale participatory varietal trials, leading to the formal release of traditional millet varieties. The organization also documents and revives forgotten foods and indigenous crops, mapping traditional food cultures and engaging communities in conservation efforts through seed banks and custodian farmers. Their value-chain approach includes post-harvest processing, branding, marketing, and policy advocacy to create economic opportunities for farmers. Collaborations with government bodies, research institutions, and international partners support their mission, ensuring that indigenous food systems are preserved and leveraged for food security, climate resilience, and rural livelihoods.
Download the summary (5 pp.)
13/02 Community of Practice on Africa Forgotten and Underutilized Food Commodities
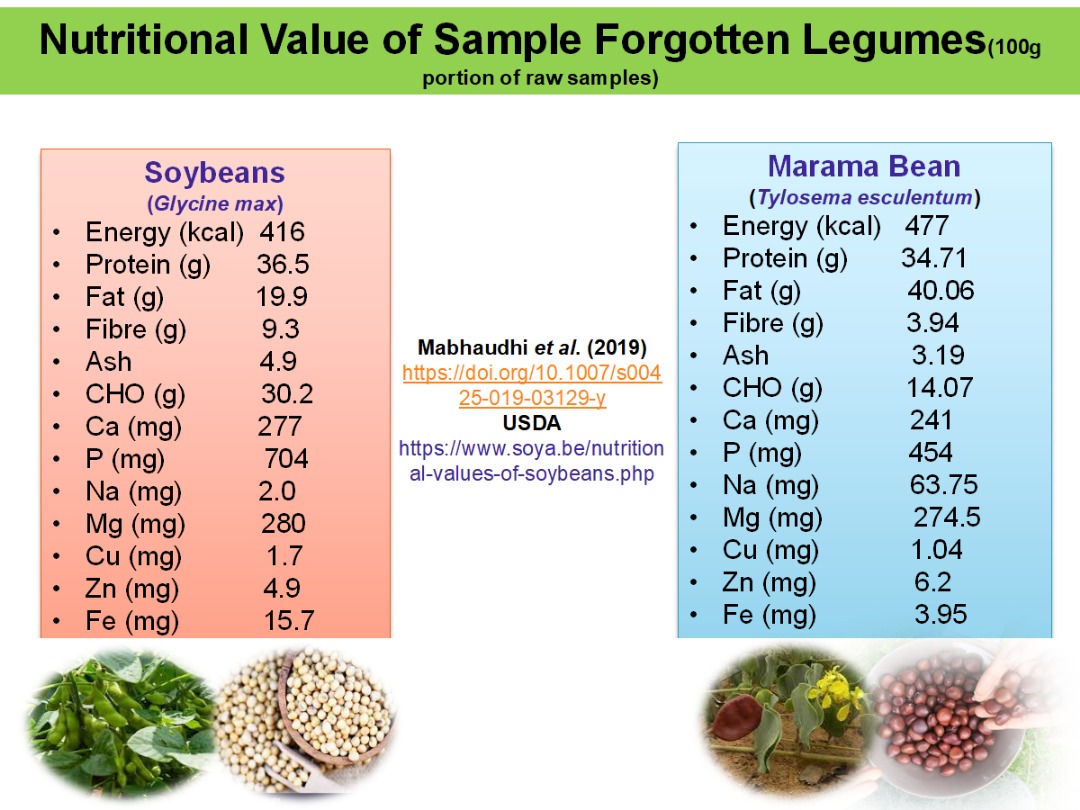
- By Wole FATUNBI, Lead Specialist: Innovation Systems and Partnerships - Forum for Agricultural Research in Africa (FARA)
The Africa Community of Practice (CoP) on Forgotten Foods, led by FARA, aims to reintegrate neglected and underutilized food commodities into Africa’s mainstream food systems to address food and nutritional insecurity. The initiative focuses on research, knowledge sharing, technology development, policy advocacy, and investment mobilization. With over 7,000 edible crop species underutilized, the CoP seeks to promote biodiversity, enhance food resilience, and improve market access for forgotten foods. Key strategies include awareness campaigns, participatory plant breeding, conservation of genetic resources, strengthening seed systems, and fostering private sector engagement. The CoP also prioritizes youth and women’s involvement, regional partnerships, and financial mechanisms to scale forgotten food initiatives. Through collaboration with research institutions, policymakers, and agribusiness stakeholders, the initiative aims to create a sustainable, inclusive, and nutrition-secure African food system.
14/02 Guided tour Genetic Resources Center, IITA, Ibadan
The Genetic Resources Center (GRC) at the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) in Ibadan, Nigeria, is dedicated to the conservation and utilization of Africa's rich plant genetic diversity.
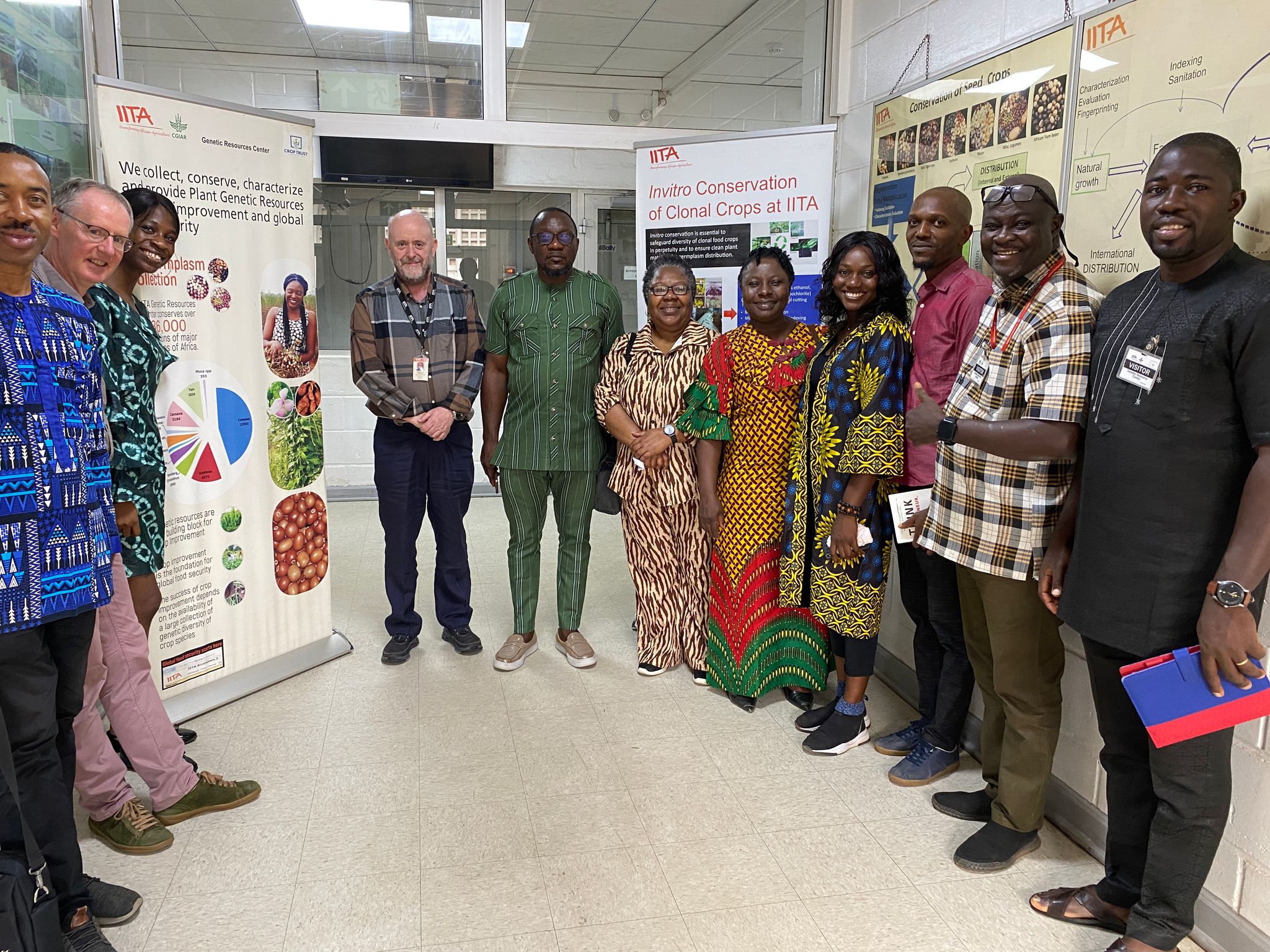

- The GRC maintains an extensive genebank that holds germplasm of major African food crops, including underutilized indigenous species often termed "forgotten foods."
- These indigenous crops, such as various orphan legumes, are preserved to ensure their availability for research, breeding, and cultivation, thereby supporting food security and agricultural sustainability across the continent.
- Recognizing the potential of these neglected crops, IITA's GRC has undertaken research to explore their nutritional benefits, adaptability, and role in diversifying food systems. A recent study highlighted the significance of indigenous African orphan legumes, emphasizing their potential to enhance food and nutrition security, promote crop diversification, and bolster climate resilience.
- By focusing on these underutilized species, the GRC aims to reintroduce them into mainstream agriculture, offering farmers alternative crops that are well-suited to local environments and resilient to changing climatic conditions.
14/02 Field visit Forgotten Foods
See: The final day was an opportunity to visit the Bodija Market, a popular open-air market located, Ibadan North, Oyo State, South Western Nigeria.

Resources:
FAO (2024) Compendium of forgotten foods in Africa: A companion publication for Integrating Africa’s forgotten foods for better nutrition 120 pp.
- Indigenous communities across Africa have used several locally adapted crops for millennia, mainly for nutrition, medicinal and ornamental purposes.
- Unfortunately, many of these crops have been progressively substituted with imported genotypes favoured by industrial agriculture. Pervasive monoculture of the exotic crops and increasingly standardised diets have partly contributed to the utter denigration of the indigenous crops, earning them the appellation of "forgotten crops.”
GFAiR policy brief: The Role of Private Sector Investment in Scaling Agricultural Innovations: Focus on Nutrition and Forgotten Foods (4pp.)
- This is an extract of a forthcoming GFAiR Insights - 40 pp.
- GFAiR is currently finalising a GFAiR Insights publication (40 pp.) on the need for agricultural research to reach out to the private (finance) sector.
- The full report includes the example of The INCITIS-FOOD consortium.
- The INCITIS research project and consortium funded by DG RTD exceptionally involves a financial partner to upscale innovation. The African Rural and Agricultural Credit Association (AFRACA) is a leading pan-african network of financial and non-financial institutions involved in promoting access to rural and agricultural finance in Africa.
- The INCITIS-FOOD Project is working on improving innovative circular food system in 6 countries across 3 African regions: East (Kenya), West (Ghana, Nigeria and Sierra Leone) and Central (Cameroun and Gabon).
- The objective of the eight living labs in six African countries is to map the landscape of food providers, manufacturers, marketers, and consumers and to help identify bottlenecks and challenges that can be addressed by the living labs.
Deffor, E. (2024) Value Chain Analysis for Selected Indigenous Vegetables in Ghana. Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Horticulture
- The FAO Sustainable Food Value Chain (SFVC) framework guided this value chain analysis. The elements of the framework provide a market-oriented and systems-based approach for measuring, analyzing, and improving the performance of food value chains (FVCs) in ways that help ensure their economic and environmental sustainability.
- Cocoyam Leaf (Kontomire), Turkey Berry (Kwahu Nsusua), Okra and Garden Eggs

Related event

11-13 February 2025. Lusaka, Zambia. Academic symposium and workshop ‘Traditional foods for the future’
2-14 February 2025. Postgraduate course: Traditional foods for the future. Local traditional foods to promote food and nutrition security: transdisciplinary approaches to advance Sustainable Development Goals
Many local traditional foods exist that are part of local culture and tradition. They are usually well suited to local agronomic practices and informal value chains and, have great potential to promote nutrition and livelihoods. However, due to specific characteristics of each of these foods and the focus on globally available alternatives, local traditional foods have been understudied. This has hampered their use to promote nutrition and livelihoods within the local context of many LMIC. To promote traditional foods, a symposium is specifically focusing on local traditional (fermented) foods in Southern Africa. This symposium covers six topics and their interrelationships:
- Food fermentation: processing and product functionality
- Microbial ecology of the environment and fermented foods
- Food environment, diets and health
- Personal entrepreneurial context
- Value chains and institutions
- Consumer needs and preference

